I had a great opportunity to participate in the OpenInfra Summit Asia 2024, held from September 3-4. This OpenInfra Summit was the first of its kind organized by OpenInfra Asia, a regional hub established in 2023 to support open-source communities across Asia, making it a highly meaningful event. Additionally, it was co-hosted by the Open Compute Project (OCP) Foundation, a leading open-source foundation, which underscored the event’s scale and enriched its program with the joint effort of two major global open-source communities. Over 240 speakers delivered more than 190 sessions covering a broad range of topics, including Linux, OpenStack, Kubernetes, and over 30 other open-source projects. Along with more than 1,500 attendees from over 30 countries, I was able to attend insightful and valuable sessions.
The sessions with insightful information were primarily offered in English and Korean, with the majority in English. It was intriguing to see that Flitto’s simultaneous translation service offered translations in more than 16 languages to support attendees less familiar with English. QR codes for the translation service were placed in front of session rooms, allowing easy and convenient access without the need to download the app.
Many participants could smoothly follow the translated content on their own devices, receiving translations almost instantly as the speakers presented.
Keynotes
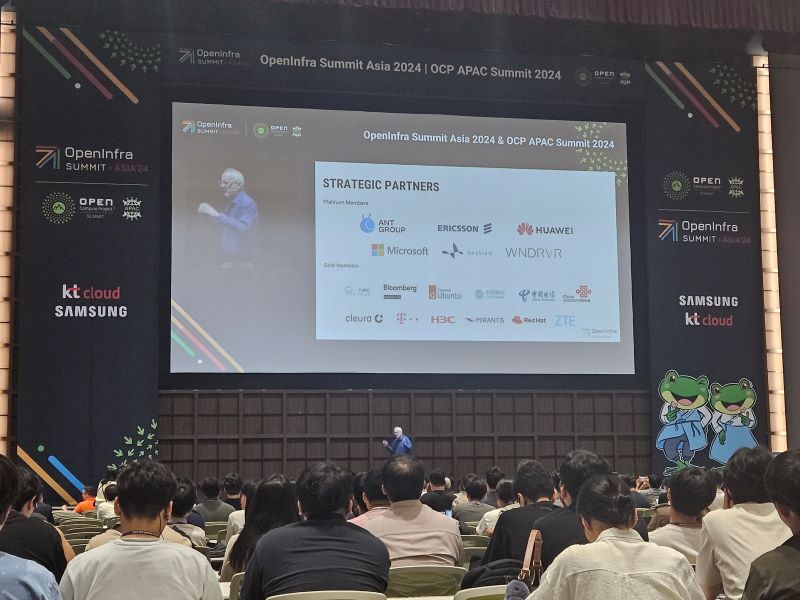

Mark Collier, COO of the OpenInfra Foundation, delivered an impressive keynote where he clearly outlined four key trends in infrastructure. Below is the summary of the keynote.
1. Digital Sovereignty
There is a growing interest and need to know where data is stored, who has access to it, and what legal jurisdiction it falls under. This issue is no longer just a personal concern but has become critical for national institutions and governments as well. A notable example is French banks adopting OpenStack to manage their data’s location, access, and applicable legal frameworks independently. This trend of major institutions seeking exclusive control over their data is growing on a global scale.
This trend is also emerging in the hardware sector, with RISC-V being a prime example. RISC-V is an open-source Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) instruction set architecture developed at UC Berkeley in 2010. With RISC-V, designers can customize and design processors tailored to specific end applications.
In essence, there’s a current industry-wide trend toward having permanent access, control, and flexibility over the programs and hardware in use. As a result, open-source and open technology have become more crucial than ever.
2. License Changes
Terraform
The unexpected license change for Terraform had a negative impact on the market, but open-source projects can present the workaround. In response to this shift, the open-source project Open Tofu emerged to serve as a reliable alternative to Terraform, ensuring continuity and trust for its users.
VMware
With VMware’s license changes, there is a growing interest in migrating from VMware to OpenStack. A prominent example is GEICO, a major U.S. auto insurance company, which recently replaced VMware with OpenStack to build a large-scale cloud infrastructure, garnering considerable attention. Mark Collier even shared a QR code for a white paper on migration during the keynote.
3. Security Concerns
A recent revelation that 87% of operating container images have critical or high-severity vulnerabilities has raised serious concerns. To address this issue, the Kata Containers project, hosted by the OpenInfra Foundation, is gaining significant attention. Kata Containers offers lightweight virtualization that combines the speed of containers with the security of virtual machines, striking a balance between speed and security. Due to its effectiveness in securing container environments, Microsoft Azure, NVIDIA, and AWS are investing in and supporting Kata Containers.
4. AI Redefining Infra
AI is gaining significant attention with companies racing to acquire as many GPUs as possible to build massive data center capacity. This substantial investment in AI infrastructure has positioned OpenStack as a crucial player in supporting AI workloads.
These four major trends—digital sovereignty, license changes, security concerns, and artificial intelligence—are driving greater interest and investment in open-source technologies, fueling the growth of the open-source community.
Sessions
The OpenInfra Asia Summit 2024 featured numerous sessions covering a wide range of in-depth topics. Among them, I attended a session, titled “OpenStack of NHN Cloud from a Network Perspective.”, by Sungwoo Park, Network Infrastructure Development Team Lead at NHN Cloud. This session gave valuable insights into real-world applications of OpenStack and strategies NHN Cloud used to address its limitations. Here’s a summary of some key points from the session.
1. Openstack of NHN Cloud from a network perspective

NHN Cloud established its network and launched services in 2015 using OpenStack’s Neutron. However, in the early stages, Neutron’s basic functions proved insufficient for efficiently and reliably operating NHN Cloud’s network services, as it did not support redundancy, failover, or scaling capabilities. This session delved into how NHN Cloud overcame these limitations.
Neutron’s basic structure consists of a QRouter, an OVS integration bridge, and a Linux bridge located between them within each compute node. Security groups are implemented through IP tables within this setup. However, as the number of security rules increased, it became challenging to trace code errors and troubleshoot issues, creating a significant maintenance burden. Additionally, since the Linux bridge operates only at Layer 2 of the OSI model, it was limited in handling traffic based on routing or IP addresses.
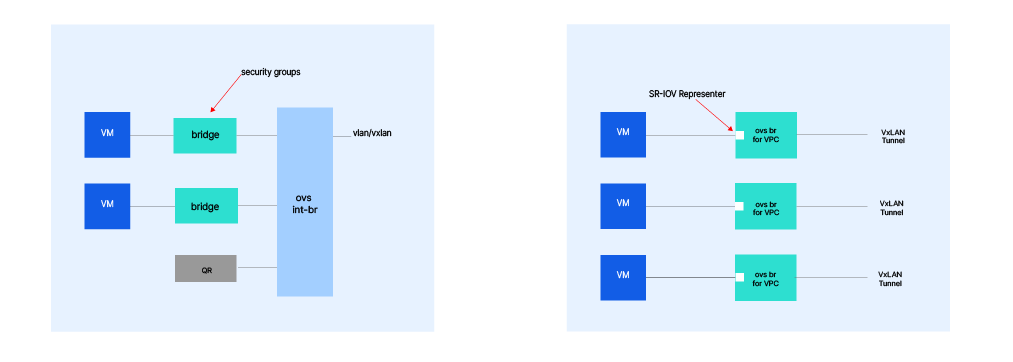
To address these issues, NHN Cloud removed the Linux bridge and QRouter from the compute nodes, replacing them with a VPC-specific bridge setup. By segmenting the network for each VxLAN and connecting each bridge accordingly, NHN Cloud established a more efficient network architecture. A particularly impressive improvement was achieved by connecting NVIDIA’s SR-IOV Representer to the OVS bridge, which significantly boosted I/O performance. SR-IOV (Single Root I/O Virtualization) is a technology that enables multiple virtual machines to simultaneously utilize a single physical PCI Express device, making it highly valuable in virtualized environments.
As mentioned above, the QRouter was removed from the compute nodes, and the router was relocated to the top of the rack as a solution to its limitations. This adjustment allowed each rack to function as a large hypervisor, simplifying the structure of compute nodes and enabling maximum efficiency.
However, this architecture created a new challenge, as all traffic became concentrated on the top-of-rack routers. To address this, NHN Cloud developed a custom vSwitch, capable of handling an impressive 5 million packets per second (5 mpps) per core.
The decision to transition from VLAN to VxLAN was also interesting. With a growing customer base, NHN Cloud needed to support multiple Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) in a public environment, a task for which VLAN was not well-suited. Additionally, VxLAN resolved redundancy issues and eliminated physical distance constraints, making it an ideal solution for scaling their network.
Security and Stability
In terms of security and stability, NHN Cloud implemented several improvements. By combining Neutron’s default Security Groups with Network ACLs, they created an environment where communication could occur without servers needing to store client state information. Additionally, they enhanced network communication flexibility by connecting a VPN Gateway, enabling remote host communication without an Internet Gateway.
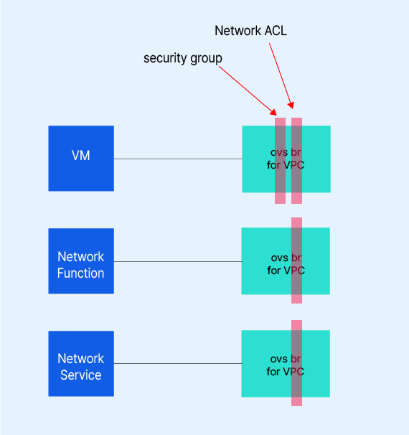
Since launching services in 2015, NHN Cloud has introduced numerous plugins and custom-developed agents to extend OpenStack Neutron’s capabilities. Through the session, it was clear how NHN Cloud innovatively tackled existing network issues, strengthening both service stability and security. This also highlighted the complexities involved in managing cloud network infrastructure.
2. Bridging the Gap Between Community and Contributing Orgs
In addition to lecture-style sessions, the summit also offered forum-style sessions where participants could freely discuss topics together. One such session, titled “Bridging the Gap Between Community and Contributing Orgs,” served as an open platform for sharing ideas to further invigorate the open-source community. The main focus was on ways to enhance communication between new and existing contributors and improve the contributor experience for everyone involved.
With many people from various countries contributing to OpenInfra projects, this session was charged with enthusiasm for overcoming communication barriers and embracing diversity within the community.
OpenStack’s Role in the Future
The OpenInfra Summit Asia 2024 once again highlighted the critical role of the open-source community in driving innovation within the cloud industry.
The spotlight on migration from VMware to OpenStack emphasized the growing global interest among companies in adopting OpenStack as a scalable, secure, and cost-effective solution.
Additionally, as demand grows for sustainable infrastructure to support high-performance computing like AI, the OpenInfra community showed it is ready to address these global challenges with innovative solutions. This summit further raised expectations for the future of open-source infrastructure and the sustainable development of technology.
- OpenInfra Asia Summit 2024 Recap - November 8, 2024
)










